Quest Diagnostics – New York Centre Street
Ste 207
New York, NY 10013-4552
United States
Quest Diagnostics – New York Chinatown
Ste 702
New York, NY 10013-4637
United States
Quest Diagnostics – New York 210 East 86Th Street
Ste 602
New York, NY 10028-3003
United States
Quest Diagnostics – Nyc-26Th St – Employer Drug Testing Not Offered
Ste 201
New York, NY 10001-6975
United States
Quest Diagnostics – New York East 57Th Street
Ste 1530
New York, NY 10022-2100
United States
Quest Diagnostics – New York West 14Th Street – Employer Drug Testing Not Offered
3Rd Fl
New York, NY 10014-5002
United States
Quest Diagnostics – Nyc Midtown – Employer Drug Testing Not Offered
New York, NY 10036-4702
United States
Apb Services, Inc – Apb Services Inc – Drug Testing Only (Preferred)
1St Floor
New York, NY 10019-5008
United States
Quest Diagnostics – New York 3Rd Avenue
Ste 303
New York, NY 10010-7454
United States
Quest Diagnostics – New York East 76Th Street
New York, NY 10021-1844
United States
About STD Testing Facilities in New York NY
Where in NYC Are You?
Find more localized testing in Bronx NY, Brooklyn NY, Queens NY, and Staten Island NY.
Maximum Convenience for STD Testing in New York City
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)—or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)—are no joke. However, STD testing and treatment doesn't have to be complicated. We want to make the process of finding clinics that have the STD tests you need as convenient for you as possible. Information like contact numbers, business hours, and more is available for many local facilities. The power to choose an STD clinic that's right for you has never been easier!
Order an STD Test
HIV Quick Facts About New York City, New York
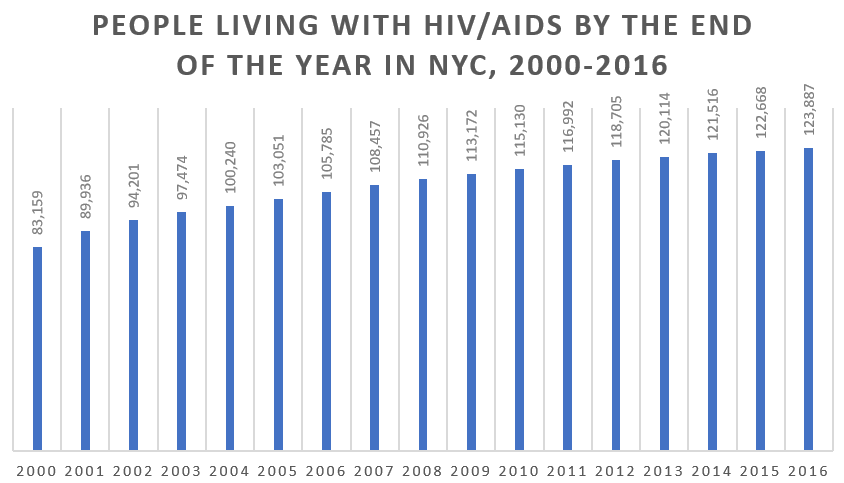
As of 2015, the CDC estimates that 1.1 million people have HIV in the United States.[1] The CDC also reports that 16% of new HIV diagnoses occurred in the Northeast in 2017.[2] By the end of 2016, health officials estimated that 123,887 people were living with HIV/AIDS in NYC.[3]
STD Quick Facts About New York State
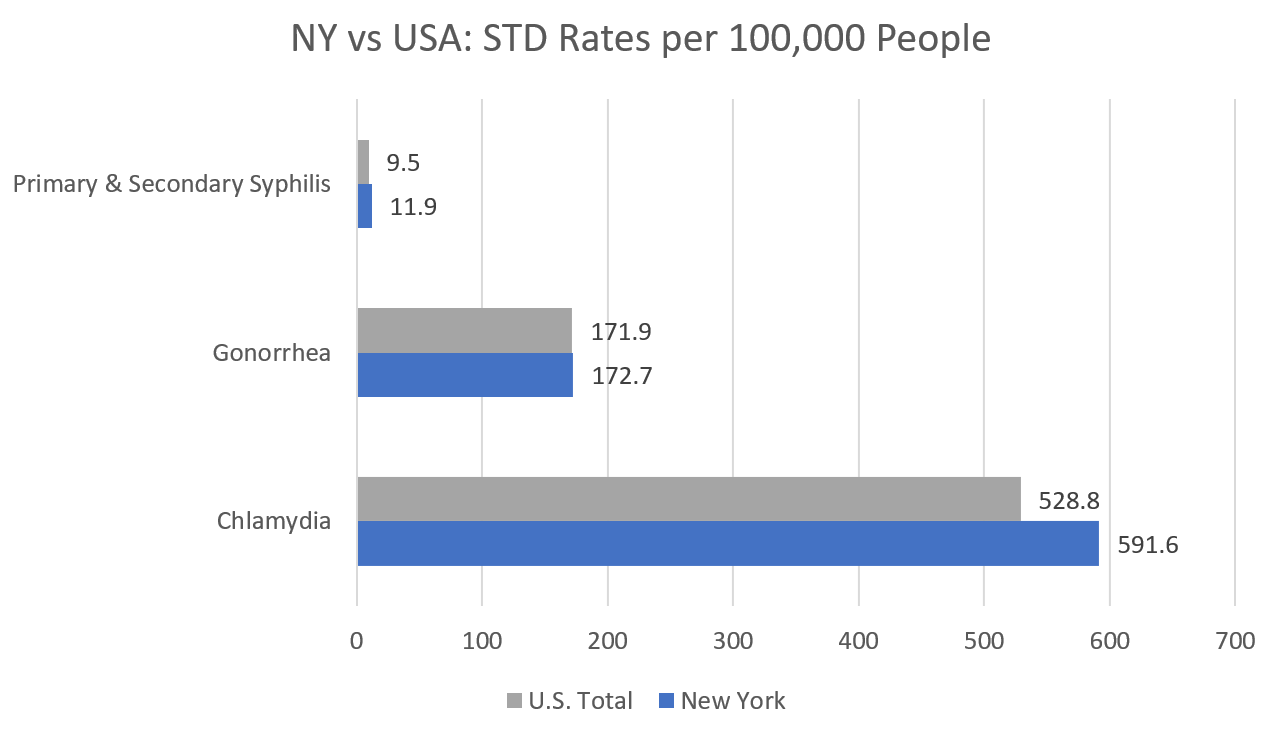
Chlamydia and gonorrhea were two of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in the United States of America in 2017. Did you know that the CDC reported 116,814 cases of chlamydia and 34,099 cases of gonorrhea in New York during that year? This means that New York ranked #9 for chlamydia and #21 for gonorrhea out of all 50 states based on the 2017 STD Surveillance Report's ranking methodology.[4]
Unfortunately, many people don't notice symptoms of these two incredibly common infections. An STD test is the only way to know for sure know the true state of your sexual health.
What Is the Difference Between an STI and STD?
STI means sexually transmitted infection. STD means sexually transmitted disease. They both refer to infections that you can contract from sexual activities.
Who Is at Risk?
Certain demographics are considered to be at higher risk of contracting some infections. That being said, ANYONE who engages in vaginal, anal, and/or oral sex—especially if unprotected—can contract an STD, regardless of sexual orientation, gender, or race.
What Are Common STD Symptoms?
Signs of an infection will vary by individual as well as by the specific STD(s) the person has. However, it is incredibly common for people to notice no symptoms at all. This is why checking for symptoms alone is not an accurate indicator of health.
What Do I Need to Know About Getting Tested?
You can check out our pages on the following infections:- Gonorrhea: One of the most common STDs in both the United States and the world. The last few years have seen an increase in gonorrhea cases in the US. Many infected people do not show symptoms of this STD.
- Chlamydia: Along with gonorrhea, chlamydia is one of the most common STDs in the United States. The number of people diagnosed with this infection has increased the past few years. Roughly 7 out of 10 people with this infection do not show symptoms.
- Syphilis: This STD imitates the signs of other diseases, earning its nickname "the great imitator." Syphilis is on the rise, too. The CDC reported 56,485 cases of syphilis (all stages) across the United States in 2013. By 2017, that number skyrocketed to 101,567. That's a nearly 80% increase!
- Hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C: Hep A, Hep B, and Hep C are the three most common types of viral hepatitis in the United States. While vaccines are available for Hep A and Hep B, there is no vaccine available to help prevent Hep C.
- HIV/AIDS: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV destroys the body's immune system, making it vulnerable to potentially lethal opportunistic infections. There is no cure or vaccine available for either HIV or AIDS.
- Oral herpes and genital herpes: Herpes can refer to either oral herpes (usually caused by HSV-1) or genital herpes (usually caused by HSV-2). According to the CDC, roughly 1 in 6 adults in the US have herpes.
- Trichomoniasis: Another common STD, trichomoniasis (or "trich") is often asymptomatic, or symptomless. In fact, the CDC estimates that almost 70% of people with trich don't show any symptoms.
Tests & Pricing: How Much Does STD Testing Cost?
It depends on the tests you take and whether you decide to bundle them. Some tests will be cheaper than others. For example, a hepatitis A test, hepatitis B test, and hepatitis C test here will each only cost you less than $25. Specialized tests will usually cost more than standard options. For instance, an HIV early detection test will usually cost more than a regular HIV test, but can give you accurate results about your HIV status far sooner than a standard testing method.
Bundling is a great idea not only to save money, but also to give you peace of mind. If you’re already getting tested for one infection, getting tested for other common STDs can help give you a more comprehensive view of your sexual health. Bundling a chlamydia test with a gonorrhea test is common and often results in serious savings. Even more options are available, though. Here you can get HIV type 1, HIV type 2, herpes 1, herpes 2, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C testing all for a great price.
Of course, if you visit a clinic and receive other services, your bills might be higher. Whether or not your health insurance covers certain tests, services, and/or doctor visits can also impact how much you will pay out of pocket for testing.
Because prices can vary wildly, you can contact the place you plan to test at ahead of time to get an estimate for your costs.
How Long Does STD Testing Take?
The actual process for getting tested can be simple and quick. It all depends on the test (or tests) you take. For example, you can provide a urine sample for an STD test in minutes. You might even be able to complete other screenings and get results right there in the health center office. Rapid HIV testing, for instance, can take less than 20 minutes!
Providing samples for other types of tests might take slightly longer. A syphilis test, for example, most commonly involves drawing blood at a sexual health clinic. Ultimately, how long this process takes depends on the infections you test for and the testing methods you use.
How Long Will my STD Test Results Take?
You can get fast results as quickly as in 1-2 days. Just know that testing right before a weekend or holiday can make the wait longer.
What Happens If I Test Positive?
If you test positively for a sexually transmitted disease, you should receive further instructions on what to do next when you receive your diagnosis. This will involve speaking to a licensed medical professional about treatment and also reaching out to sexual partners you may have exposed as well.
I Want Lots of Medical Information. Where Can I Get It?
New York, New York residents can get information on STDs, care, treatment, counseling, and more from their doctor, local and state public health departments, or the CDC, among other places.
[1] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (Last reviewed 19 November 2018). HIV/AIDS: Basic Statistics. Retrieved 9 April 2019, from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/statistics.html
[2] CDC. (Last reviewed 27 November 2018). HIV/AIDS: HIV in the United States by Region. Retrieved 9 April 2019, from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/statistics/overview/geographicdistribution.html
[3] HIV Epidemiology and Field Services Program, NYC DOHMH. (Table generated October 2017). Table 3: AIDS Diagnoses and Persons Living with HIV/AIDS by Year, Pre-1981 to 2016, New York City. Retrieved 10 April 2019, from PDF. PDF retrieved from https://www1.nyc.gov/site/doh/data/data-sets/hiv-aids-annual-surveillance-statistics.page
[4] CDC. (2017). 2017 STD Surveillance Report. Retrieved 9 April 2019, from https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/SRtables.pdf
This site is not to act as professional medical advice or diagnose any condition. Specific comments, questions, or concerns should be directed toward a licensed health-care professional.