What Is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs), or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), in the world. Some people may also know it as “the clap” or “the drip.”
How Common Is Gonorrhea. . .
. . . in the United States?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that gonorrhea is the second-most reported STD in the United States, right behind chlamydia. The CDC estimates 820,000 new cases occur in the U.S. every year. The vast majority of people who catch this STD are between 15 and 24.[1]
Gonorrhea and other common STD cases have increased steadily in recent years.[2] This may be due to a combination of factors. Why are STD rates are increasing? Speculations include less funding for sexual health programs and STD prevention resources, poor access to affordable health care, antibiotic resistance, less safe sexual practices, and not getting tested.[3][4][5]
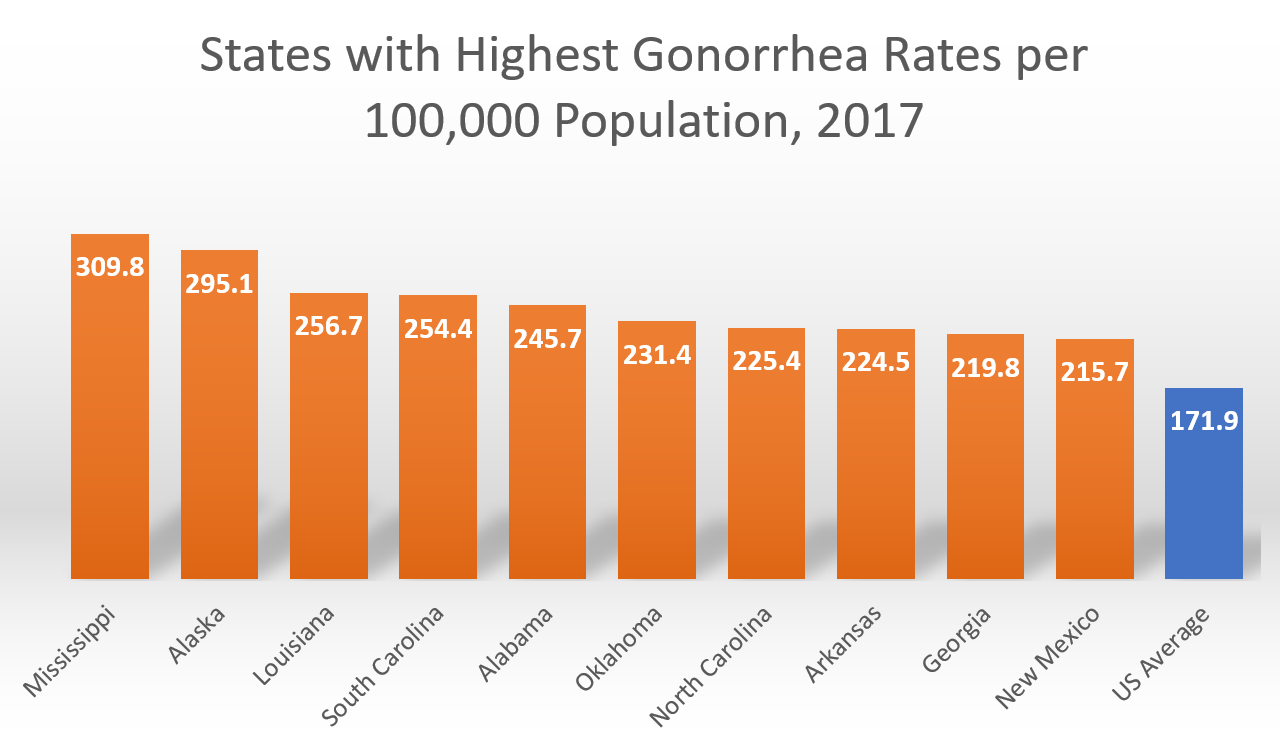
Based on data reported by the CDC.
. . . around the world?
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 78 million people around the globe become infected with this STD every year.[5]
How Is Gonorrhea Transmitted?
Gonorrhea transmission occurs primarily through sexual contact. However, a mother can also pass the infection to her unborn child during childbirth.
There’s a lot of confusion as to how people can get this STD. Many people think only vaginal sex can spread this STD. That isn’t true! Vaginal, anal, and oral sex can all spread this infection. Some people also make the mistake of thinking that hormonal birth control (like “the pill”) can prevent STDs. This is also false. The pill can only help prevent pregnancy; it does not protect against infections.
Factors that can increase the risk of catching gonorrhea include:
- A previous case of gonorrhea
- Past or present STDs
- Multiple sexual partners
- Incorrect condom use
- No condom use
- Condom use only during vaginal sex
- Current drug and alcohol abuse
- Pregnancy
Use our FREE STD Risk Calculator to calculate potential risk.
What Are Some Gonorrhea Prevention Methods?
There are plenty of ways to reduce your chances of catching STDs. Some great methods include:
- Abstaining from sexual contact
- Using condoms or other protective barriers properly
- Using new protective barriers for every sexual act
- Talking with sexual partners about testing
- Getting tested regularly
Can I Only Get Gonorrhea in my Genitals?
No, you can get this STD in many places. The bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae causes gonorrhea to grow and multiply in mucus membranes. This means the bacteria thrive in conditions that are warm and moist. This makes the reproductive system in women especially vulnerable. Both men and women can become infected in the urethra, mouth, throat, eyes, and anus.[1]
Who Can Get Gonorrhea?
This STD is more common among younger people, especially those under 24.[1] As such, the CDC recommends sexually active women 25 or younger receive a yearly gonorrhea screening. However, anyone having unsafe sex is at risk of gonorrhea.

What Are Common Gonorrhea Symptoms?
When do symptoms of gonorrhea begin to show?
For women, symptoms begin to appear within 2 to 10 days. Men begin to experience symptoms after 1 to 14 days.[1] Symptoms may take a little longer to appear, though.
What are noticeable gonorrhea symptoms in women?
- Lower abdominal pain
- Pelvic pain
- Painful urination
- Spotting between periods
- Whitish or greenish-yellow discharge from the vagina
- Spotting after sex
- Vulva swelling
- Swollen glands in the throat
- Burning sensation in the throat
- Red, itchy eyes
What are noticeable gonorrhea symptoms in men?
- Burning sensation during urination
- Painful or swollen testicles
- Swollen glands in the throat
- Burning sensation in the throat
- Whitish or greenish-yellow discharge from the penis
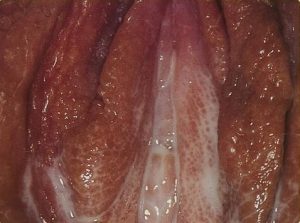
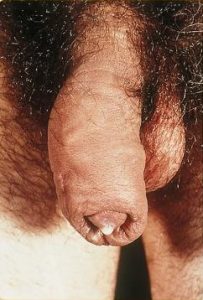
What Does Gonorrhea Discharge Look Like?
The following are gonorrhea discharge pictures. They show infections of both the vagina and penis. The following images are graphic and may be disturbing to some people. Do not attempt a self-diagnosis based on the following images.
I don’t notice any symptoms. This means I don’t have gonorrhea, right?
Wrong. Many people show no signs of gonorrhea. It is incredibly common for women especially to not show any symptoms. This means you could have gonorrhea and not even know it based on symptoms alone!
What Are the Dangers of Untreated STDs?
Without knowing their actual STD status, infected people can spread their STD to others without knowing it. Gonorrhea isn’t just an inconvenient STD. If it isn’t treated, it could lead to nasty, long-term health problems.
What Happens If I Don’t Treat Gonorrhea?
Untreated infections can cause serious and permanent health issues for both men and women. Those with untreated gonorrhea are also at a higher risk of contracting and transmitting HIV.[5]
What are the consequences for untreated women?
Women can commonly get both chlamydia and gonorrhea.[6][7] Like gonorrhea, chlamydia can also appear symptomless and cause long-term problems if not treated.
Gonorrhea can also spread to the uterus and fallopian tubes. If this happens, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).[1][5][7] PID symptoms range from mild to severe, depending on the individual. PID can mean chronic (long-term) pelvic pain, internal abscesses, and permanent damage of the fallopian tubes. The end result can be infertility.
Besides infertility, PID can mean a higher risk of dangerous ectopic pregnancies. This type of pregnancy is where the fetus grows outside the uterus. This pregnancy can never deliver a living baby, and it can have fatal consequences for the mother.
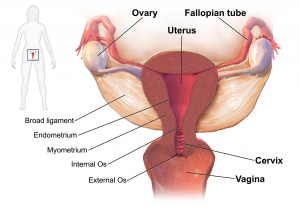
What are the consequences for untreated pregnant women and their babies?
An untreated pregnant woman can pass gonorrhea to her baby during vaginal delivery. What happens to a baby born with this STD? It can mean blindness, joint infections, or even potentially fatal blood infections.[1]
What are the consequences for untreated men?
Untreated gonorrhea in men can result in a condition known as epididymitis. Epididymitis is a painful condition of the testicles that may lead to infertility. Gonorrhea can also spread to the prostate. This can cause difficult and painful urination because of scarring inside the urethra.
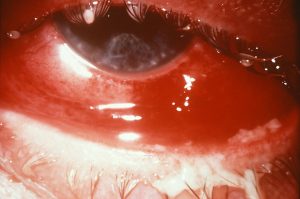
Is Gonorrhea Curable?
In most cases, yes. Simple doses of antibiotics often are an effective means of gonorrhea treatment.
However, there is growing concern about the rise of antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea. Experts partly attribute this resistance to health officials inappropriately giving out antibiotics.[5] This can happen for a number of reasons.
One common way is for a doctor to make a diagnosis based on symptoms alone. The problem here is that some gonorrhea signs can look like symptoms of other diseases.[5][6] So, a doctor can easily misdiagnose someone with gonorrhea and give them antibiotics specifically for this STD. This is a problem when the patient actually has something else.[5] A lab test is the only way to know with 100% certainty if you have gonorrhea or not.
Not fully completing a round of antibiotics can also lead to antibiotic resistance. Don’t think that you can ignore certain parts of your doctor’s advice. Always follow the treatment directions your doctor gives you exactly. Your doctor is the expert, after all, and just wants to help you feel better.
I’ve Had Gonorrhea Once. Can I Get It Again?
Yes. Having this STD once does not protect you or a partner from getting it again in the future.
How Does Gonorrhea Testing Work?
Gonorrhea testing often involves urine samples. However, swabs taken from the rectum and mouth are also common means of collecting samples. There are different ways to test these samples. One such way is through a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT), a newer form of testing. It can find traces of gonorrhea bacteria in urine or other bodily fluid samples.
How Are Samples Collected?
Doctors can collect samples in their offices. They can take a swab from areas like the cervix, urethra, anus, throat, or eye. You can also pee into a container that the doctor or nurse provides you.
Where Can I Find a Gonorrhea Testing Facility Near Me?
Fortunately, most places that offer STD screenings can test for this disease.
Find a gonorrhea testing facility now.
Where Can I Order a Gonorrhea Test?
You can order a test for gonorrhea here. Select the infections you wish to test for, follow the check-out instructions, and then save your order information and Lab Requisition form. Bring either your code or Requisition form with you to your chosen testing location.
CDC – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
HIV – Human Immunodeficiency Virus
PID – Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
STI – Sexually Transmitted Infection
STD – Sexually Transmitted Disease
WHO – World Health Organization
STDTestingFacilities does not suggest that the authors/sources of the images used on this page endorse this site. Images are for illustrative purposes only. No images used on this site should be used as diagnostic tools.
“Gonorrhea Testing – Where Can I Get Tested?” and website resources should neither act as nor replace professional medical information or advice. Always consult a licensed health care professional regarding medical questions or concerns.